
by Simon Ng | Oct 8, 2015 | Economics Tuition, International Trade, JC Economics Notes, Macroeconomics |
A quota refers to the direct control of import demand, which will lower supply of imports, thus reducing quantity demand for imports. The restriction of the quantity of imported goods will create an artificial shortage that leads to the increase in price of the...

by Simon Ng | Oct 8, 2015 | Economics Tuition, International Trade, JC Economics Notes, Macroeconomics |
Purpose of comparative advantage The concept of comparative advantage explains how countries which are efficient in production can specialise and trade with countries which are inefficient so as to maximise total production and consumption, based on the concept of...

by Simon Ng | Oct 8, 2015 | Economics Tuition, International Trade, JC Economics Notes, Macroeconomics |
The factors that limit free trade can be seen in terms of the artificial barriers to trade, and natural barriers to entry. The artificial barriers to trade refers to protectionism, in which countries implement policies that prevent the import of foreign goods into the...
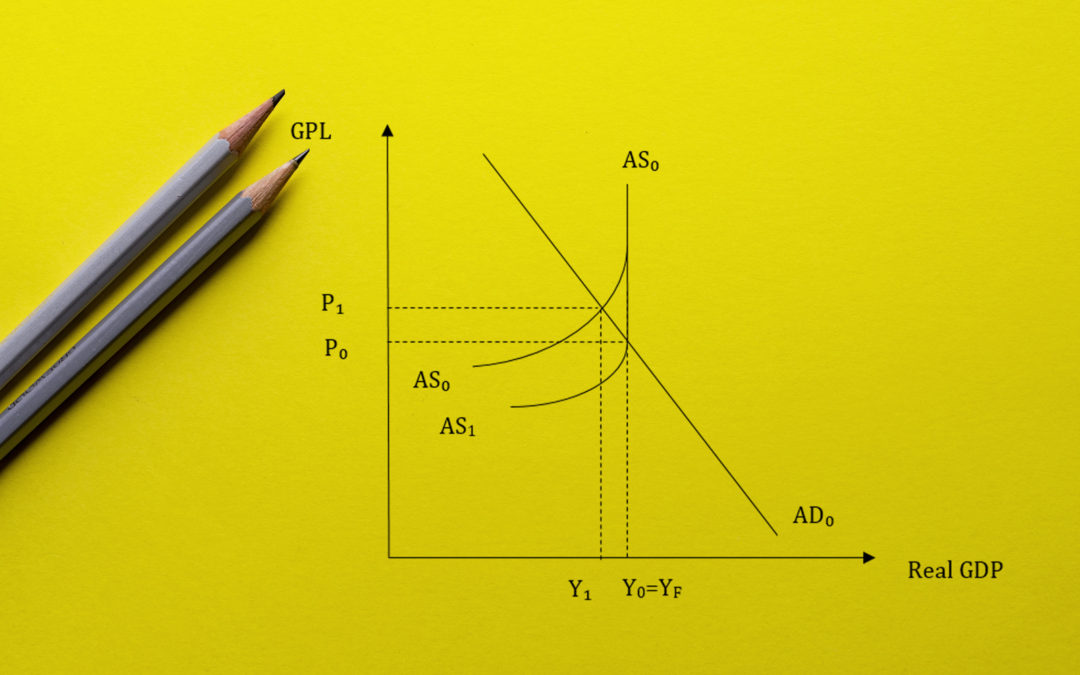
by Simon Ng | Aug 20, 2015 | Economics Tuition, Inflation, JC Economics Notes, Macroeconomics |
Cost-push inflation occurs when there is a rise in cost of production which will lead a fall in the aggregate supply that will lead to an excess demand condition, contributing to increase in price level. When the cycle becomes cyclical, it will develop as wage-price...

by Simon Ng | Aug 20, 2015 | Economics Tuition, Inflation, JC Economics Notes, Macroeconomics, Unemployment |
When there is a rise in oil prices, the cost of production is increased which will lower aggregate supply, resulting in an excess demand condition, thus raising general price level. Hence, cost-push inflation arises. An oil price hike leads to inflationary pressures....






